Condensation polymerization offers the possibility of constructing polymer molecules of accurately known structure. Predict the degree of polymerization if 75 of monomer end groups have been converted to polymer.

Carothers Theory L Carothers Developed A Simple Method
32 pp 39-49 1936 P.

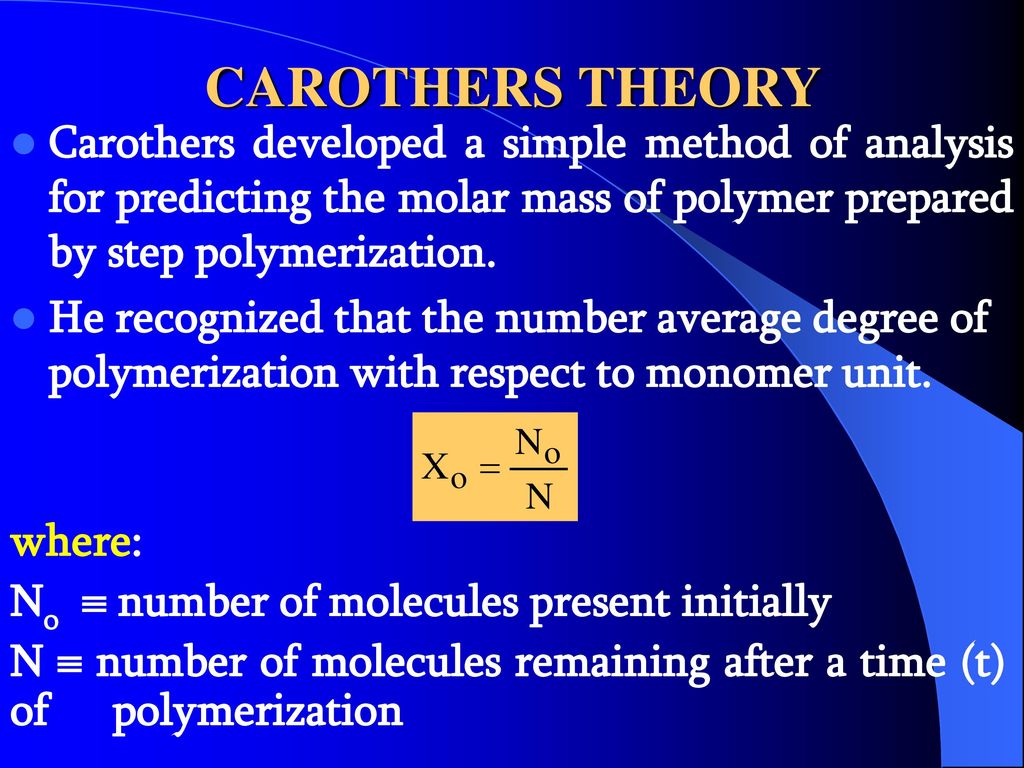
. An equation attributed to Carothers 1 relates the number. N 0 is the number of molecules present initially N is the number of unreacted molecules at time t p is also a measure of the extent of reaction or yield. In step-growth polymerization the DP is calculated by Carothers equation which is defined for linear and branched molecules.
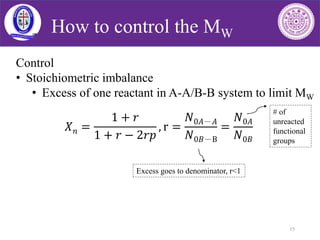
Carothers equation is applicable only to stoichiometric mixtures of addition monomers or if only one type of functional group undergoes polymerization as it is the case with chain growth. FloryStockmayer theory is a theory governing the cross-linking and gelation of step-growth polymers. The theory was initially conceptualized by Paul Flory in 1941 and then was further developed by.
This equation was originally proposed by Carothers and is often referred to as the Carothers equation. The simplest case refers to the formation of a strictly linear polymer by the reaction usually by condensation of two. A Word on MWD for Nonlinear Polymerizations 9.
The Flory-Stockmayer theory represents an advancement from the Carothers equation allowing for the identification of the gel point for polymer synthesis not at stoichiometric balance. A few days after starting work he. In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization X n.
For linear polymer formed by the reaction usually by condensation of two monomers in equimolar quantities the equation of DP is. Polymer molecular weight in a step-growth polymerization is determined by the fractional conversion p of the monomer during the polymerization. X n is also the average chain length in monomer units p N 0-NN 0 where.
Step-growth polymerization vs chain growth to be covered in more detail later in the course extent of reaction number-average degree of polymerization. Two monomers in equimolar quantities. P c 2 f avg.
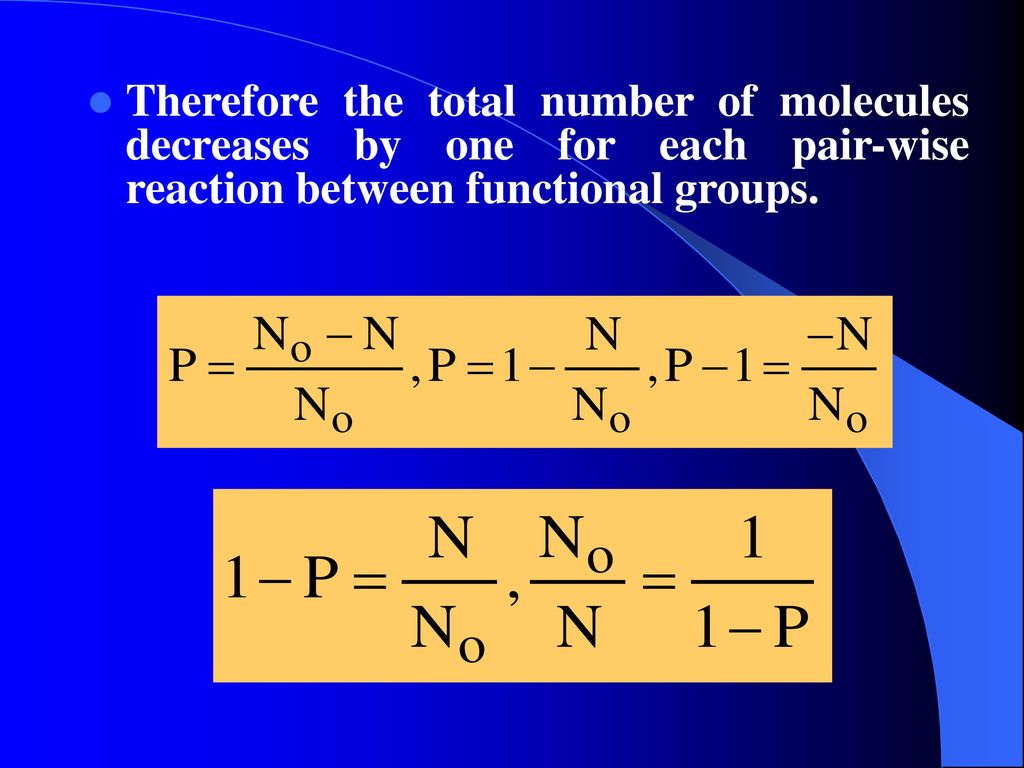
The Carothers Equation High Molecular weights are hard to get this way If there are N omolecules at time 0 and N remaining at time t then the amount reacted is N 0 -N and we can define p as the conversion or fraction reacted then as P N o N N o or N N o 1 P If DP is the average degree of polymerization N 0. The simplest case refers to the formation of a strictly. Carothers believed that polymers were molecules hooked together end-to-end in long chains by ordinary bonds.
You may be surprised really how high extent of reaction needs to be in order to get polymers of any significant length especially as your reactant ratio deviates more greatly from. This equation is based on general stochastic insights and gives the degree of polymerization or number average chain length ie xn for a given A or equivalently B FG conversion p with r 1 ignoring intramolecular reactions. After integration and substitution from Carothers equation the final form is the.
Monomers oligomers and polymers. This equation was originally suggested by Carothers in 1936 and is often referred to as the Carothers equation. Other Polymers of Interest Obtained by Step-Growth.
Carothers equation is used to illustrate the extent of reaction for linear polycondensation or polyaddition polymerization reactions. In polycondensations the number-average degree of polymer- ization DP can be expressed as DP 1 r1 r 2rp where p is the extent of the polymerization and r is the stoichiometric ratio between the comonomers. Flory Journal of the American Chemical Society 58 1877-1885 1936 Paul L.
If X n describes the number of average chain length and P describes the extent of the reaction then starting with N 0 as the number of molecules at the beginning of the polymerization after some time has elapsed N is the number of molecules. There are several versions of this equation proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935. The total includes all degrees of polymerization.
This equation was originally proposed by Carothers and is often referred to as. Thus the second term of the Carother equation vanishes and the critical extent of the reaction p c is given by. 1 This equation reaches an asymptotic value at p p 1 and requires in practice a final evaluation at p 099.
Furthermore the synthesis follows Carothers equation DP 1 1-p which describes the degree of polymerization DP as a function of conversion p the fraction of monomer transformed to polymer. One way to express molecular. In the nineteenth century physicists such as Maxwell Boltzmann and Kelvin researched and experimented with creep and recovery of glasses metals and rubbersViscoelasticity was further examined in the late twentieth century when synthetic polymers were engineered and used in a variety of applications.
This relationship is called the Carothers equation in honor of Wallace Carothers the DuPont chemist who invented nylon. Pn Approach 8 Network Formation. For the case of linear polymers - two monomers in equimolar quantities.
Derivation of the Carothers equation for molecular mass as a function of the extent of the reaction p and reactant ratio r. To test his theory he proposed to create polymers by using well-known chemical reactions to join together many small molecules. N In step-growth polymerization the Carothers Equation Carothers Equation gives the degree of polymerization X n for a given fractional monomer conversion p Odain 2004.
This equation was proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935. So now we have an equivalent way of expressing degree of polymerization in terms of the fraction converted. In step-growth polymerization in order to achieve a high degree of polymerization and hence molecular weight X n a high fractional monomer conversion p is required according to Carothers equation For example a monomer conversion of p 99 would be required to achieve X n 100.
In his pioneering work from 1929 carothers described a vision for polycondensation that expressed the requirement for reactive monomeric functional groups to form a new bond through the elimination of a small molecule or condensate12 the early work explored the reversible nature of polycondensation reactions and strategies to circumvent the. Network Formation and Gelation. Derivation of the Carothers.
Segmented and Block Copolymers from Step Condensation Methods 7 Crosslinking and Branching. In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization X n for a given fractional monomer conversion p. Flory Principles of Polymer Chemistry Ithaca New york 1953.
This equation shows that a high monomer conversion is required to achieve a high degree of polymerization. The Carothers equation is based on the assumption of equal reactivity of functional groups which means that the reactivity of one functional group of a bifunctional monomer is the same irrespective of whether the other functional group has reacted and the.

Macromolecular Chemistry Lecture 5 Step Growth Chain Growth

Polymer Chemistry Malcolm P Stevens Ppt Download

Step Growth Polymerization The Carothers Equation And The Flory Schulz Distribution Montoguequiz Com

Step Growth Polymerization The Carothers Equation And The Flory Schulz Distribution Montoguequiz Com

Degree Of Polymerization Of Polymers Materials Today
Chapter 9 Kinetics Of Chain And Step Growth Polymerization
Carothers Theory Carothers Developed A Simple Method Of Analysis For Predicting The Molar Mass Of Polymer Prepared By Step Polymerization He Recognized Ppt Download
Carothers Theory Carothers Developed A Simple Method Of Analysis For Predicting The Molar Mass Of Polymer Prepared By Step Polymerization He Recognized Ppt Download

Lecture 2 The Carothers Equation Youtube

Spring 2007 Chap 8 Polycondensation Reactions Classification By

Spring 2007 Chap 8 Polycondensation Reactions Classification By

General Approaches To Polymer Synthesis 1 Addition Chain

Degree Of Polymerization Of Polymers Materials Today

Introduction To Polymers Lecture 5 5 Step Growth Molecular Weight Part 2 Youtube

Carothers Theory Carothers Developed A Simple Method Of Analysis For Predicting The Molar Mass Of Polymer Prepared By Step Polymerization He Recognized Ppt Download

Step Growth Polymerization Wikiwand

Synthetic Organic Polymers Convenor Dr Fawaz Aldabbagh Polymers

